Data Collection
pyrene
CAS Number: 129-00-0
Basic Information
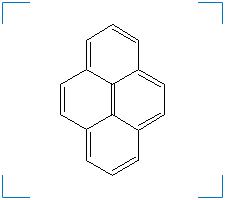 Synonym(s): Benzo[def]phenanthrene; beta-pyrene; Pyrene; Pyrene[def]phenanthrene; Pyrene
Synonym(s): Benzo[def]phenanthrene; beta-pyrene; Pyrene; Pyrene[def]phenanthrene; Pyrene
Formula: C16H10
Molecular Weight: 202.255
Boiling Point (°C): 404
Melting Point (°C): 156
Contaminant Type: pyrene is a polyclyclic aromatic hydrocarbon.
Notes: MONOCLINIC PRISMATIC TABLETS FROM ALCOHOL OR BY SUBLIMATION; PURE PYRENE IS COLORLESS; PALE YELLOW PLATES (WHEN RECRYSTALLIZED FROM TOLUENE); Colorless solid (tetracene impuritites give yellow color)
Solubility (in water)
- Solubility:
1.32E-01
mg/kg
ao
Temperature (°C): 25
- Solubility:
1.48E-01
mg/kg
ao
Temperature (°C): 25
- Solubility:
1.29E-01
mg/kg
ao
Temperature (°C): 25
- Solubility:
1.30E-06
g/100ml
d
- Solubility:
1.65E-01
mg/kg
ao
Temperature (°C): 29
- Solubility:
1.60E-01
mg/l
ak
Temperature (°C): 26
- Solubility:
3.20E-02
mg/l
ak
Half-Life (in soil unless otherwise noted)
- t1/2:
3; 10; 35
days
ak
Environment: degradation in a soil system at initial conc between 3 and 500
- t1/2:
2
months
ak
Temperature (°C): 20
Environment: biodegradation in sandy loam in the dark at 700 mg/kg
- t1/2:
0.58-5.2
years
f
Temperature (°C): 10-30
Environment: Based upon aerobic soil die-away test data
- t1/2:
3
years
ak
Temperature (°C): 20
Environment: abiotic degradation in sandy loam in the dark at 700 mg/kg
Toxicity Effects
- Organism Type:
Fish
ak
Common Name: Fathead minnow
Scientific Name: Pimephales promelas
Toxicity: 10 mg/l
Test: 1d mortality
Soil Organic Carbon/Water Partition Coefficients
Octanol-Water Partition Coefficients
Work Cited
|
d
|
ChemFinder. Cambridge MA: CambridgeSoft Corporation. Retrieved November, 2003 from http://chemfinder.cambridgesoft.com
|
|
f
|
Howard, P. H., R. S. Boethling, W. F. Jarvis, W. M. Meylan, and E. M. Michalenko. 1991. Handbook of Environmental Degradation Rates. Lewis Publishers., Chelsea, MI.
|
|
aj
|
RAIS. 2005. Risk Assessment Information System. Pages retrieved April, 2005 from http://risk.lsd.ornl.gov/tox/rap_toxp.shtml. U.S. Department of Energy, Office of Environmental Management, Oak Ridge Operations (ORO) Office, Bechtel Jacobs Company LLC, Oak Ridge, TN.
|
|
ak
|
Verschueren, K. 2001. Handbook of Environmental Data on Organic Chemicals, 4th edition. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York.
|
|
ao
|
Santodonato, J., P. Howard, D. Basu, S.D. Lee, Si Duk, and L. Grant. 1981. Health and ecological assessment of polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons. Pages 1-364 in Journal of environmental pathology and toxicology, volume 5(1). Park Forest South, Ill. : Pathotox Publishers.
|
|
ay
|
Nagpal, N. K. 1993. Ambient Water Quality Criteria For Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs). Pages retrieved April 2005 from http://www.env.gov.bc.ca/wat/wq/BCguidelines/pahs/index.html. British Columbia Ministry of Environment.
|