Data Collection
Ametryne
CAS Number: 834-12-8
Basic Information
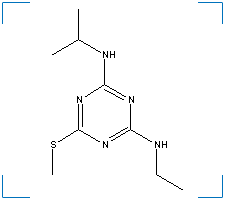 Synonym(s): 1,3,5-Triazine, 2-(ethylamino)-4-(isopropylamino)-6-(methylthio)-; 2-Ethylamino-4-isopropylamino-6-methylthio-s-triazine; Ametrex; Ametryne; Ametryn ; Cemerin; Evik; Evik 80W; Gesapax
Synonym(s): 1,3,5-Triazine, 2-(ethylamino)-4-(isopropylamino)-6-(methylthio)-; 2-Ethylamino-4-isopropylamino-6-methylthio-s-triazine; Ametrex; Ametryne; Ametryn ; Cemerin; Evik; Evik 80W; Gesapax
Formula: C9H17N5S
Molecular Weight: 227.33
Melting Point (°C): 84 - 85
Contaminant Type: Ametryne is an herbicide.
Solubility (in water)
- Solubility:
185
ppm
e
Temperature (°C): 20
Half-Life (in soil unless otherwise noted)
- t1/2:
6
months
al
Temperature (°C): 15
- t1/2:
4.5
months
al
Temperature (°C): 30
- t1/2:
70-250
days
h
Environment: depending upon soil type and weather conditions
Toxicity Effects
- Organism Type:
Fish
e
Common Name: Goldfish
Scientific Name: Carassius auratus
Toxicity: 14 mg/l
Test: 96h LC50
- Organism Type:
Fish
k
Common Name: Carp
Scientific Name: Cyprinus carpio
Toxicity: <1.0 mg/l
Test: 96h LC50
- Organism Type:
Fish
e
Common Name: Bluegill
Scientific Name: Lepomis macrochirus
Toxicity: 4.1 mg/l
Test: 96h LC50
- Organism Type:
Fish
e
Common Name: Rainbow trout
Scientific Name: Oncorhynchus mykiss
Toxicity: 8.8 mg/l
Test: 96h LC50
- Organism Type:
Mammals
h
Common Name: Mouse
Scientific Name: Muridae (Family)
Toxicity: 945 mg/kg
Test: LD50
- Organism Type:
Mammals
h
Common Name: Rat
Scientific Name: Muridae (Family)
Toxicity: 508 mg/kg
Test: LD50
- Organism Type:
Mammals
g
Common Name: Rat
Scientific Name: Muridae (Family)
Toxicity: 1950 mg/kg
Test: LD50
- Organism Type:
Mammals
k
Common Name: Rat
Scientific Name: Muridae (Family)
Toxicity: 1110 mg/kg
Test: LD50
- Organism Type:
Molluscs
k
Common Name: Oyster
Toxicity: >1.0 ppm
Test: 96h LC50
Soil Organic Carbon/Water Partition Coefficients
- Koc:
214
ml/g
k
Formulation: Aguadilla loamy sand
pH Value: 7.4
- Koc:
368
ml/g
k
Formulation: Aguirre clay loam
pH Value: 9
- Koc:
386
ml/g
k
Formulation: Alonso clay
pH Value: 5.1
- Koc:
120
ml/g
k
Formulation: Altura laom
pH Value: 8
- Koc:
326
ml/g
k
Formulation: Bayamon sandy clay laom
pH Value: 4.7
- Koc:
255
ml/g
k
Formulation: Catalina clay
pH Value: 4.7
- Koc:
172
ml/g
k
Formulation: Catano sand
pH Value: 7.9
- Koc:
345
ml/g
k
Formulation: Cayagua sandy loam
pH Value: 5.2
- Koc:
472
ml/g
k
Formulation: Cialitos clay loam
pH Value: 5.4
- Koc:
430
ml/g
k
Formulation: Coloso clay loam
pH Value: 5.7
- Koc:
136
ml/g
k
Formulation: Coto clay
pH Value: 7.7
- Koc:
190
ml/g
k
Formulation: Fe clay loam
pH Value: 7.5
- Koc:
959
ml/g
k
Formulation: Fortuna silty clay loam
pH Value: 5.4
- Koc:
276
ml/g
k
Formulation: Fraternidad clay
pH Value: 6.3
- Koc:
336
ml/g
k
Formulation: Fraternidad clay
pH Value: 5.9
- Koc:
146
ml/g
k
Formulation: Guanica clay
pH Value: 8.1
- Koc:
480
ml/g
k
Formulation: Humata silty clay loam
pH Value: 4.5
- Koc:
376
ml/g
k
Formulation: Josefa silty loam
pH Value: 6
- Koc:
703
ml/g
k
Formulation: Juncos silty clay
pH Value: 6.2
- Koc:
287
ml/g
k
Formulation: Mabi clay
pH Value: 7
- Koc:
198
ml/g
k
Formulation: Mabi clay laom
pH Value: 5.7
- Koc:
173
ml/g
k
Formulation: Mercediat silty clay
pH Value: 8.1
- Koc:
621
ml/g
k
Formulation: Moca clay
pH Value: 5.8
- Koc:
550
ml/g
k
Formulation: Mucara loam
pH Value: 5.8
- Koc:
311
ml/g
k
Formulation: Nipe clay loam
pH Value: 5.7
- Koc:
316
ml/g
k
Formulation: Pandura sandy loam
pH Value: 5.7
- Koc:
158
ml/g
k
Formulation: Rio Pedras silty clay
pH Value: 4.9
- Koc:
279
ml/g
k
Formulation: San Anton loam
pH Value: 6.7
- Koc:
253
ml/g
k
Formulation: Sand
pH Value: 5.6
- Koc:
278
ml/g
k
Formulation: Sandy loam
pH Value: 6.1
- Koc:
225
ml/g
k
Formulation: Silty loam
pH Value: 6.9
- Koc:
171
ml/g
k
Formulation: Silty loam
pH Value: 7
- Koc:
230
ml/g
k
Formulation: Silty loam
pH Value: 7
- Koc:
837
ml/g
k
Formulation: Toa loam
pH Value: 5.3
- Koc:
612
ml/g
k
Formulation: Toa sandy loam
pH Value: 6
- Koc:
774
ml/g
k
Formulation: Talante sandy loam
pH Value: 5.1
- Koc:
254
ml/g
k
Formulation: Vega Alta sandy loam
pH Value: 5
- Koc:
643
ml/g
k
Formulation: Via loam
pH Value: 5.1
- Koc:
2.23-2.44
k
Formulation: log
Octanol-Water Partition Coefficients
- Log Kow:
2.6; 2.69; 2.82; 3.07
e
- Log Kow:
676
h
Notes: Source did not specify type of partition coeffecient or if value was the log
Work Cited
|
e
|
Verschueren, K. 1996. Handbook of Environmental Data on Organic Chemicals, 3rd edition. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York.
|
|
g
|
Meister, R. T., and C. Sine (Ed). 2003. Crop Protection Handbook, volume 89. Meister Publishing Company, Willoughby, OH.
|
|
h
|
Extension Toxicology Network. Pages retrieved November, 2003 from http://ace.orst.edu/info/extoxnet/. Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR.
|
|
k
|
Montgomery, J. H. 1993. Agrochemicals Desk Reference: Environmental Data. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton, FL.
|
|
al
|
Speclab.com. 2003. Spectrum chemcial fact sheet. Pages retrieved April 2005 from http://www.speclab.com/compound/. Spectrum Laboratory Inc, Ft. Lauderdale, FL and Savannah, GA.
|