Data Collection
Propazine
CAS Number: 139-40-2
Basic Information
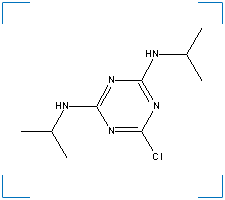 Synonym(s): 1,3,5-Triazine, 2,4-bis(isopropylamino)-6-chloro-; 1,3,5-Triazine, 2-chloro-4,6-bis(isopropylamino)-; 2-Chloro-4,6-bis(isopropylamino)-s-triazine; 6-Chloro-N,N'-bis(1-methylethyl)-1,3,5-triazine-2,4-diamine; Gesamil; Milogard; Milogard 4L; Milo-Pro; Milo-
Synonym(s): 1,3,5-Triazine, 2,4-bis(isopropylamino)-6-chloro-; 1,3,5-Triazine, 2-chloro-4,6-bis(isopropylamino)-; 2-Chloro-4,6-bis(isopropylamino)-s-triazine; 6-Chloro-N,N'-bis(1-methylethyl)-1,3,5-triazine-2,4-diamine; Gesamil; Milogard; Milogard 4L; Milo-Pro; Milo-
Formula: C9H16ClN5
Molecular Weight: 230.09
Melting Point (°C): 212 - 214
Contaminant Type: Propazine is an herbicide.
Solubility (in water)
- Solubility:
8.6
mg/l
e
Temperature (°C): 20
- Solubility:
5
mg/l
h
Temperature (°C): 20
- Solubility:
8.5
mg/l
k
Temperature (°C): 20
Half-Life (in soil unless otherwise noted)
- t1/2:
62
days
al
pH Value: 4.8
Environment: Hatzenbuhl soil
- t1/2:
127
days
al
pH Value: 6.5
Environment: Neuhofen soil
Toxicity Effects
- Organism Type:
Crustaceans
e
Common Name: Daphnia
Scientific Name: Daphnia magna
Toxicity: 11 mg/l
Test: 2d IC50
- Organism Type:
Fish
e
Common Name: Goldfish
Scientific Name: Carassius auratus
Toxicity: >32 mg/l
Test: LC50
- Organism Type:
Fish
h
Common Name: Bluegill
Scientific Name: Lepomis macrochirus
Toxicity: >100 mg/l
Test: 96h LC50
- Organism Type:
Fish
e
Common Name: Bluegill
Scientific Name: Lepomis macrochirus
Toxicity: >100 mg/l
Test: LC50
- Organism Type:
Fish
h
Common Name: Rainbow trout
Scientific Name: Oncorhynchus mykiss
Toxicity: 18 mg/l
Test: 96h LC50
- Organism Type:
Fish
e
Common Name: Rainbow trout
Scientific Name: Oncorhynchus mykiss
Toxicity: 17 mg/l
Test: LC50
- Organism Type:
Fish
g
Common Name: Rainbow trout
Scientific Name: Oncorhynchus mykiss
Toxicity: 17.5 mg/l
Test: LC50
- Organism Type:
Mammals
h
Common Name: Guinea pig
Toxicity: 1200 mg/kg
Test: LD50
- Organism Type:
Mammals
k
Common Name: Rat
Scientific Name: Muridae (Family)
Toxicity: >5000 mg/kg
Test: LD50
Formulation: 80% formulation
- Organism Type:
Mammals
g
Common Name: Rat
Scientific Name: Muridae (Family)
Toxicity: >7000 mg/kg
Test: LD50
- Organism Type:
Mammals
h
Common Name: Mouse
Scientific Name: Muridae (Family)
Toxicity: 3180 mg/kg
Test: LD50
- Organism Type:
Mammals
k
Common Name: Rat
Scientific Name: Muridae (Family)
Toxicity: 3840 mg/kg
Test: LD50
- Organism Type:
Mammals
h
Common Name: Rat
Scientific Name: Muridae (Family)
Toxicity: 3840 - >7000 mg/kg
Test: LD50
Soil Organic Carbon/Water Partition Coefficients
- Koc:
88
ml/g
k
Formulation: Bates silty loam
pH Value: 6.5
- Koc:
157
ml/g
k
Formulation: Baxter silty clay loam
pH Value: 6
- Koc:
181
ml/g
k
Formulation: Chillum silty loam
pH Value: 4.6
- Koc:
263
ml/g
k
Formulation: Clarksville silty clay loam
pH Value: 5.7
- Koc:
101
ml/g
k
Formulation: Cumberland silty loam
pH Value: 6.4
- Koc:
104
ml/g
k
Formulation: Eldon silty loam
pH Value: 5.9
- Koc:
55
ml/g
k
Formulation: Evouettes
pH Value: 6.1
- Koc:
116
ml/g
k
Formulation: Gerald silty loam
pH Value: 4.7
- Koc:
135
ml/g
k
Formulation: Grundy silty clay loam
pH Value: 5.6
- Koc:
149
ml/g
k
Formulation: Hagerstown silty clay loam
pH Value: 5.5
- Koc:
363
ml/g
k
Formulation: Hickory Hill silt
- Koc:
162
ml/g
k
Formulation: Knox silty loam
pH Value: 5.4
- Koc:
49
ml/g
k
Formulation: Lakeland loamy sand
pH Value: 6.2
- Koc:
192
ml/g
k
Formulation: Lebanon silty loam
pH Value: 4.9
- Koc:
256
ml/g
k
Formulation: Lindley loam
pH Value: 4.7
- Koc:
29
ml/g
k
Formulation: Lintonia loamy sand
pH Value: 5.3
- Koc:
263
ml/g
k
Formulation: Marian silty loam
pH Value: 4.6
- Koc:
124
ml/g
k
Formulation: Marshall silty clay loam
pH Value: 5.4
- Koc:
130
ml/g
k
Formulation: Menfro silty loam
pH Value: 5.3
- Koc:
152
ml/g
k
Formulation: Newtonia silty loam
pH Value: 5.2
- Koc:
114
ml/g
k
Formulation: Oswego silty clay loam
pH Value: 6.4
- Koc:
101
ml/g
k
Formulation: Putnam silty loam
pH Value: 5.9
- Koc:
157
ml/g
k
Formulation: Salix loam
pH Value: 6.3
- Koc:
160
ml/g
k
Formulation: Sarpy loam
pH Value: 7.1
- Koc:
208
ml/g
k
Formulation: Sharkey clay
pH Value: 5
- Koc:
135
ml/g
k
Formulation: Shelby loam
pH Value: 4.3
- Koc:
176
ml/g
k
Formulation: Soil 1
- Koc:
192
ml/g
k
Formulation: Soil 2
- Koc:
170
ml/g
k
Formulation: Soil 3
- Koc:
92
ml/g
k
Formulation: Soil 4
- Koc:
145
ml/g
k
Formulation: Soil 5
- Koc:
103
ml/g
k
Formulation: Soil 6
- Koc:
121
ml/g
k
Formulation: Summit silty clay
pH Value: 4.8
- Koc:
231
ml/g
k
Formulation: Union silty loam
pH Value: 5.4
- Koc:
144
ml/g
k
Formulation: Vertroz
pH Value: 6.7
- Koc:
244
ml/g
k
Formulation: Wabash clay
pH Value: 5.7
- Koc:
174
ml/g
k
Formulation: Waverly silty loam
pH Value: 6.4
- Koc:
147
ml/g
k
Formulation: Wehadkee silty loam
pH Value: 5.6
- Koc:
1.69-2.56
k
Formulation: log
Work Cited
|
e
|
Verschueren, K. 1996. Handbook of Environmental Data on Organic Chemicals, 3rd edition. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York.
|
|
g
|
Meister, R. T., and C. Sine (Ed). 2003. Crop Protection Handbook, volume 89. Meister Publishing Company, Willoughby, OH.
|
|
h
|
Extension Toxicology Network. Pages retrieved November, 2003 from http://ace.orst.edu/info/extoxnet/. Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR.
|
|
k
|
Montgomery, J. H. 1993. Agrochemicals Desk Reference: Environmental Data. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton, FL.
|
|
al
|
Speclab.com. 2003. Spectrum chemcial fact sheet. Pages retrieved April 2005 from http://www.speclab.com/compound/. Spectrum Laboratory Inc, Ft. Lauderdale, FL and Savannah, GA.
|