Data Collection
Terbacil
CAS Number: 5902-51-2
Basic Information
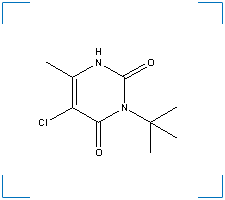 Synonym(s): 3-tert-Butyl-5-chloro-6-methyluracil; 5-Chloro-3-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-6-methyl-2,4(1H,3H)-pyrimidinedione; 5-Chloro-3-tert-butyl-6-methyluracil; DPX-D732; Geonter; Herbicide 732; Pyrimidinedione, 5-chloro-3-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-6-methyl-; Sinbar; Sinbar 80W
Synonym(s): 3-tert-Butyl-5-chloro-6-methyluracil; 5-Chloro-3-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-6-methyl-2,4(1H,3H)-pyrimidinedione; 5-Chloro-3-tert-butyl-6-methyluracil; DPX-D732; Geonter; Herbicide 732; Pyrimidinedione, 5-chloro-3-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-6-methyl-; Sinbar; Sinbar 80W
Formula: C9H13ClN2O2
Molecular Weight: 216.65
Melting Point (°C): 175 - 177
Contaminant Type: Terbacil is an herbicide.
Solubility (in water)
- Solubility:
710
ppm
g
Temperature (°C): 25
Half-Life (in soil unless otherwise noted)
- t1/2:
2-5
months
al
Environment: aerobically incubated soils
- t1/2:
5-7
months
al
Environment: in top soil after applying 4.5 kg/hectare
Toxicity Effects
- Organism Type:
Birds
h
Common Name: Quail
Scientific Name: Phasianidae (Family)
Toxicity: >2250 mg/kg
Test: LD50
- Organism Type:
Crustaceans
h
Common Name: Shrimp
Toxicity: 49 mg/l
Test: LC50
- Organism Type:
Crustaceans
h
Common Name: Daphnia
Scientific Name: Daphnia magna
Toxicity: 65 mg/l
Test: LC50
- Organism Type:
Crustaceans
h
Common Name: Fiddler crab
Scientific Name: Uca sp.
Toxicity: 1000 mg/l
Test: 48h LC50
- Organism Type:
Fish
h
Common Name: Pumpkinseed
Scientific Name: Lepomis gibbosus
Toxicity: 86 mg/l
Test: 48h LC50
- Organism Type:
Fish
h
Common Name: Bluegill
Scientific Name: Lepomis macrochirus
Toxicity: 102.9 mg/l
Test: 96h LC50
- Organism Type:
Fish
h
Common Name: Rainbow trout
Scientific Name: Oncorhynchus mykiss
Toxicity: 46.2 mg/l
Test: 96h LC50
- Organism Type:
Mammals
g
Common Name: Rat
Scientific Name: Muridae (Family)
Toxicity: >5000 - <7500 mg/kg
Test: LD50
- Organism Type:
Molluscs
h
Common Name: Marine oysters
Toxicity: >4.9 mg/l
Test: LC50
Soil Organic Carbon/Water Partition Coefficients
- Koc:
"41, 51"
al
Formulation: measured
- Koc:
38
ml/g
k
Formulation: Cecil sandy loam
pH Value: 5.8
- Koc:
42
ml/g
k
Formulation: Cecil sandy loam
pH Value: 5.6
- Koc:
21
ml/g
k
Formulation: Eustis fine sand
pH Value: 5.6
- Koc:
76
ml/g
k
Formulation: Glendale sandy clay loam
pH Value: 7.4
- Koc:
140
ml/g
k
Formulation: Keyport silt loam
pH Value: 5.4
- Koc:
64
ml/g
k
Formulation: Webster silty clay loam
pH Value: 7.3
- Koc:
~1.74
k
Formulation: log
Octanol-Water Partition Coefficients
- Log Kow:
1.8921
h
Notes: Source did not specify type of partition coeffecient or if value was the log
Work Cited
|
g
|
Meister, R. T., and C. Sine (Ed). 2003. Crop Protection Handbook, volume 89. Meister Publishing Company, Willoughby, OH.
|
|
h
|
Extension Toxicology Network. Pages retrieved November, 2003 from http://ace.orst.edu/info/extoxnet/. Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR.
|
|
k
|
Montgomery, J. H. 1993. Agrochemicals Desk Reference: Environmental Data. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton, FL.
|
|
al
|
Speclab.com. 2003. Spectrum chemcial fact sheet. Pages retrieved April 2005 from http://www.speclab.com/compound/. Spectrum Laboratory Inc, Ft. Lauderdale, FL and Savannah, GA.
|