Data Collection
Propoxur
CAS Number: 114-26-1
Basic Information
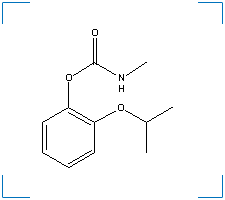 Synonym(s): 2-(1-methylethoxy)phenol methylcarbamate; 2-(1-methylethoxy)phenyl methylcarbamate; o-Isopropoxyphenyl Methylcarbamate; o-isopropoxyphenyl N-methylcarbamate; aprocarb; BAY 39007; BAY 9010; Baygon; Baygon
Synonym(s): 2-(1-methylethoxy)phenol methylcarbamate; 2-(1-methylethoxy)phenyl methylcarbamate; o-Isopropoxyphenyl Methylcarbamate; o-isopropoxyphenyl N-methylcarbamate; aprocarb; BAY 39007; BAY 9010; Baygon; Baygon
Formula: C11H15NO3
Molecular Weight: 209.27
Melting Point (°C): 91
Contaminant Type: Propoxur is an insecticide.
Notes: Solid
Solubility (in water)
- Solubility:
1.74
g/l
k
Temperature (°C): 10
- Solubility:
1.93
g/l
k
Temperature (°C): 20
- Solubility:
2.44
g/l
k
Temperature (°C): 30
Half-Life (in soil unless otherwise noted)
- t1/2:
11
days
ak
Temperature (°C): 23-26
Environment: "In a greenhouse at constant light and initial conc. of 5-10 mg/kg soil, experiment time 50 days - in sandy soil"
- t1/2:
4
days
ak
Temperature (°C): 23-26
Environment: "In a greenhouse at constant light and initial conc. of 5-10 mg/kg soil, experiment time 50 days - in organic-rich orchard soil"
- t1/2:
5
days
ak
Temperature (°C): 23-26
Environment: "In a greenhouse at constant light and initial conc. of 5-10 mg/kg soil, experiment time 50 days - in agricultural soil"
- t1/2:
27
days
ak
Temperature (°C): 23-26
Environment: "In a greenhouse at constant light and initial conc. of 5-10 mg/kg soil, experiment time 50 days - in soil from volcanic area"
- t1/2:
30
days
ak
Temperature (°C): 23-26
Environment: "In a greenhouse at constant light and initial conc. of 5-10 mg/kg soil, experiment time 50 days - in field experiments (dissipation t1/2)"
- t1/2:
0.6
days
ak
Temperature (°C): 18-22
Environment: "Aerobic biodegration half-life at an initial concentration of 2 ppm, using a mixture of nonacclimated sludge, field soil, and river sediment as inoculum, in a stirred flask, the major bacterial types in the activated sludge have been characterized as foll"
- t1/2:
1.6-28
days
f
Environment: Scientific judgement based upon estimated hydrolysis t1/2 at pH 9.0 (low t1/2) and estimated unacclimated aqueous aerobic biodegradation half-life (high t1/2)
Toxicity Effects
- Organism Type:
Birds
h
Common Name: Mallard
Scientific Name: Anas platyrhynchos
Toxicity: 10.5 mg/kg
Test: LD50
- Organism Type:
Birds
h
Common Name: Canada Goose
Scientific Name: Branta canadensis
Toxicity: 6 mg/kg
Test: LD50
- Organism Type:
Birds
h
Common Name: California quail
Scientific Name: Callipepla californica
Toxicity: 26 mg/kg
Test: LD50
- Organism Type:
Birds
h
Common Name: House finches
Scientific Name: Carpodacus mexicanus
Toxicity: 4 mg/kg
Test: LD50
- Organism Type:
Birds
h
Common Name: bobwhite quail
Scientific Name: Colinus virginianus
Toxicity: 25.9 mg/kg
Test: LD50
- Organism Type:
Birds
h
Common Name: Japanese quail
Scientific Name: Coturnix japonica
Toxicity: 28 mg/kg
Test: LD50
- Organism Type:
Birds
h
Common Name: Grouse
Scientific Name: Phasianidae (Family)
Toxicity: 120 mg/kg
Test: LD50
- Organism Type:
Birds
h
Common Name: pheasant
Scientific Name: Phasianidae (Family)
Toxicity: 20 mg/kg
Test: LD50
- Organism Type:
Birds
h
Common Name: Mourning doves
Scientific Name: Zenaida macroura
Toxicity: 4 mg/kg
Test: LD50
- Organism Type:
Crustaceans
ak
Scientific Name: Gammarus fasciatus
Toxicity: 50 µg/l
Test: 96h LC50
- Organism Type:
Crustaceans
ak
Scientific Name: Gammarus lacustris
Toxicity: 34 µg/l
Test: 96h LC50
- Organism Type:
Crustaceans
ak
Common Name: Red-swamp crayfish
Scientific Name: Procambarus clarkii
Toxicity: 1.4 mg/l
Test: 4d LC50
- Organism Type:
Fish
h
Common Name: Bluegill
Scientific Name: Lepomis macrochirus
Toxicity: 6.6 mg/l
Test: 96h LC50
- Organism Type:
Fish
h
Common Name: Rainbow trout
Scientific Name: Oncorhynchus mykiss
Toxicity: 3.7 mg/l
Test: 96h LC50
- Organism Type:
Fish
ak
Common Name: Fathead minnow
Scientific Name: Pimephales promelas
Toxicity: 8.8 mg/l
Test: 4d LC50
- Organism Type:
Mammals
k
Common Name: Rat
Scientific Name: Muridae (Family)
Gender: Male
Toxicity: 95 mg/kg
Test: LD50
- Organism Type:
Mammals
k
Common Name: Rat
Scientific Name: Muridae (Family)
Gender: Female
Toxicity: 104 mg/kg
Test: LD50
- Organism Type:
Mammals
h
Common Name: Rat
Scientific Name: Muridae (Family)
Toxicity: 100 mg/kg
Test: LD50
- Organism Type:
Mammals
h
Common Name: Mouse
Scientific Name: Muridae (Family)
Toxicity: 100 mg/kg
Test: LD50
- Organism Type:
Mammals
h
Common Name: mule deer
Scientific Name: Odocoileus hemionus
Toxicity: 100-350 mg/kg
Test: LD50
Soil Organic Carbon/Water Partition Coefficients
- Koc:
1.5
ak
Formulation: log
- Koc:
93
ml/g
k
Formulation: Clayey loam
pH Value: 6
- Koc:
53
ml/g
k
Formulation: Kanuma high clay
pH Value: 5.7
- Koc:
3
ml/g
k
Formulation: Loamy sand
pH Value: 6.6
- Koc:
76
ml/g
k
Formulation: Sandy loam
pH Value: 7.7
- Koc:
42
ml/g
k
Formulation: Silty loam
pH Value: 6.3
- Koc:
44
ml/g
k
Formulation: Silty loam
pH Value: 6.1
- Koc:
10
ml/g
k
Formulation: Silty loam
pH Value: 5.1
- Koc:
41
ml/g
k
Formulation: Tsukuba clay loam
pH Value: 6.5
- Koc:
0.48-1.97
k
Formulation: log
Octanol-Water Partition Coefficients
- Log Kow:
0.14
h
Notes: Source did not specify type of partition coeffecient or if value was the log
Work Cited
|
f
|
Howard, P. H., R. S. Boethling, W. F. Jarvis, W. M. Meylan, and E. M. Michalenko. 1991. Handbook of Environmental Degradation Rates. Lewis Publishers., Chelsea, MI.
|
|
h
|
Extension Toxicology Network. Pages retrieved November, 2003 from http://ace.orst.edu/info/extoxnet/. Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR.
|
|
k
|
Montgomery, J. H. 1993. Agrochemicals Desk Reference: Environmental Data. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton, FL.
|
|
ak
|
Verschueren, K. 2001. Handbook of Environmental Data on Organic Chemicals, 4th edition. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York.
|